Molecular identification of P-glycoprotein: a role in lens circulation?
https://iovs.arvojournals.org/article.aspx?articleid=2162635
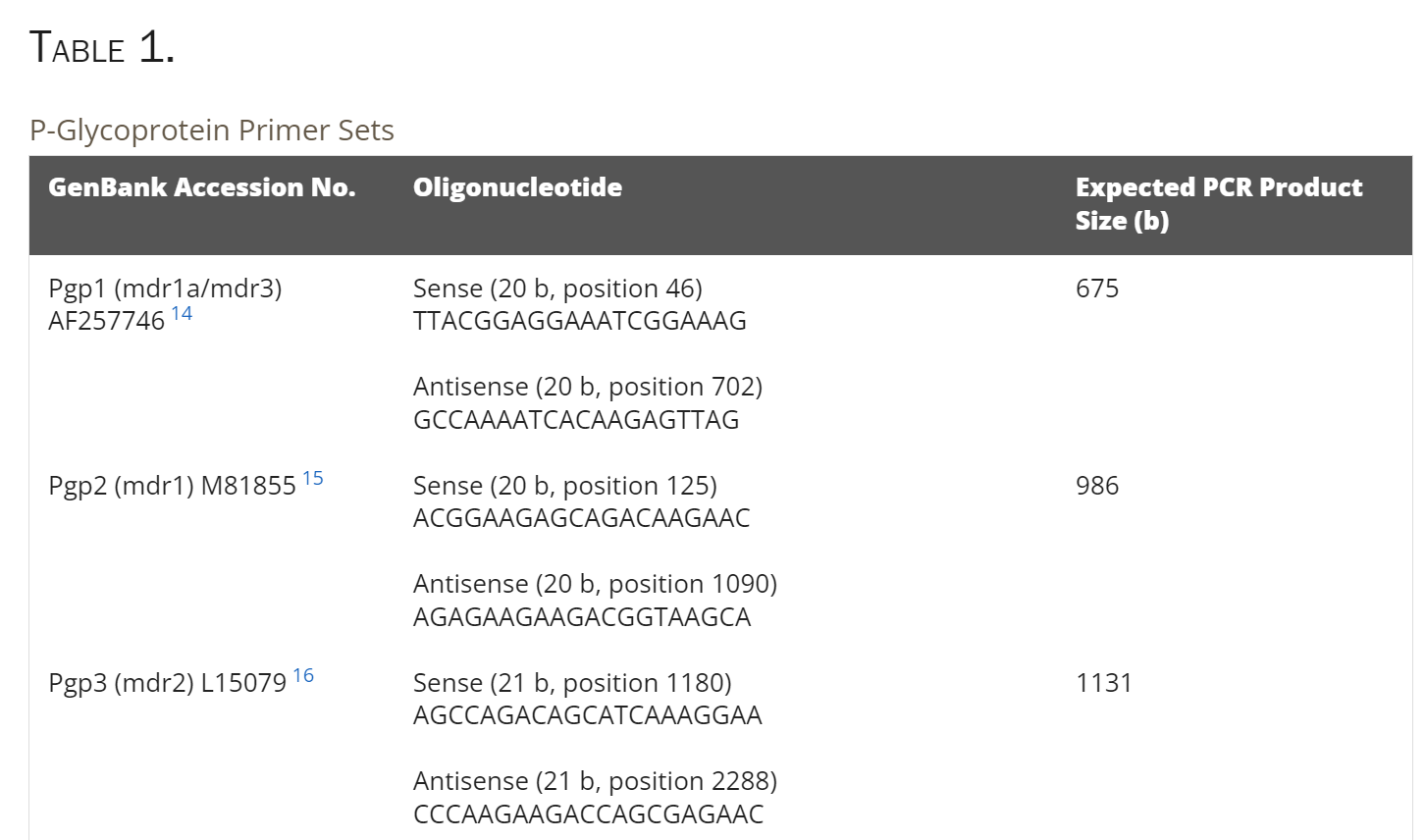
Table 1: P-glycoprotein primer sets
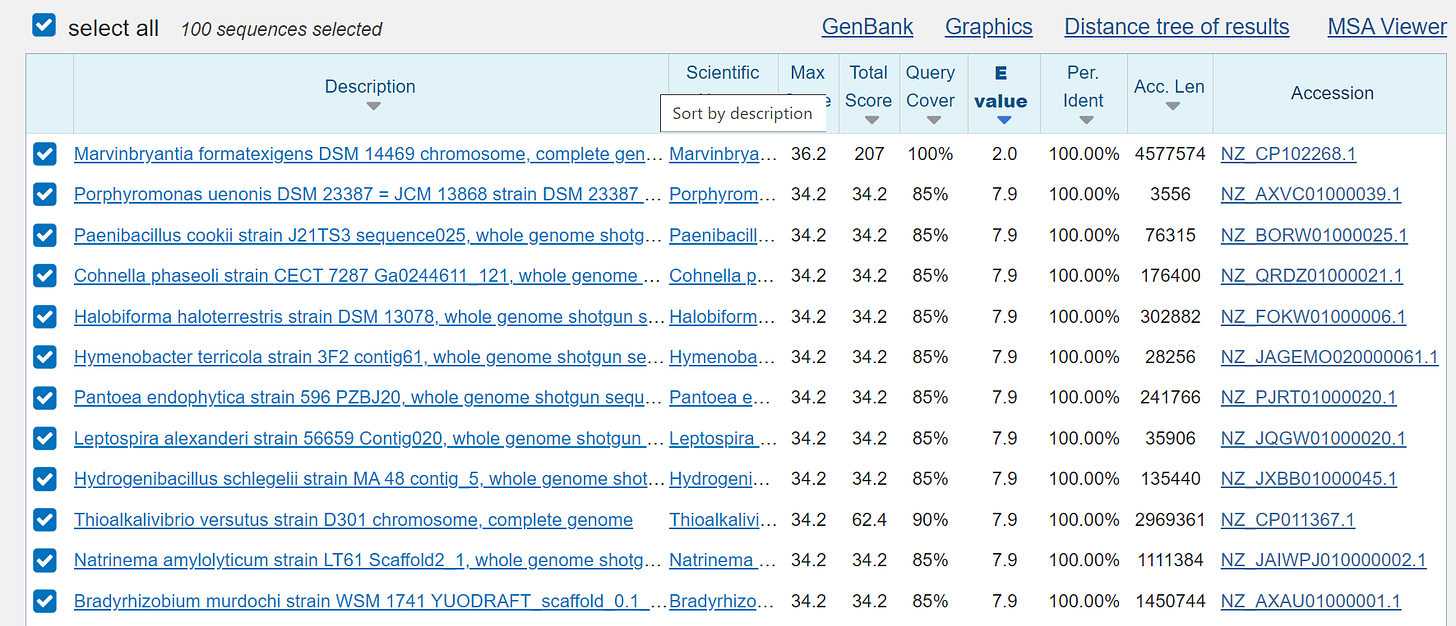
and now it will be funny if we use the BLAST search as already known:
human:
mouse:
rat:
the so-called “microbes”:
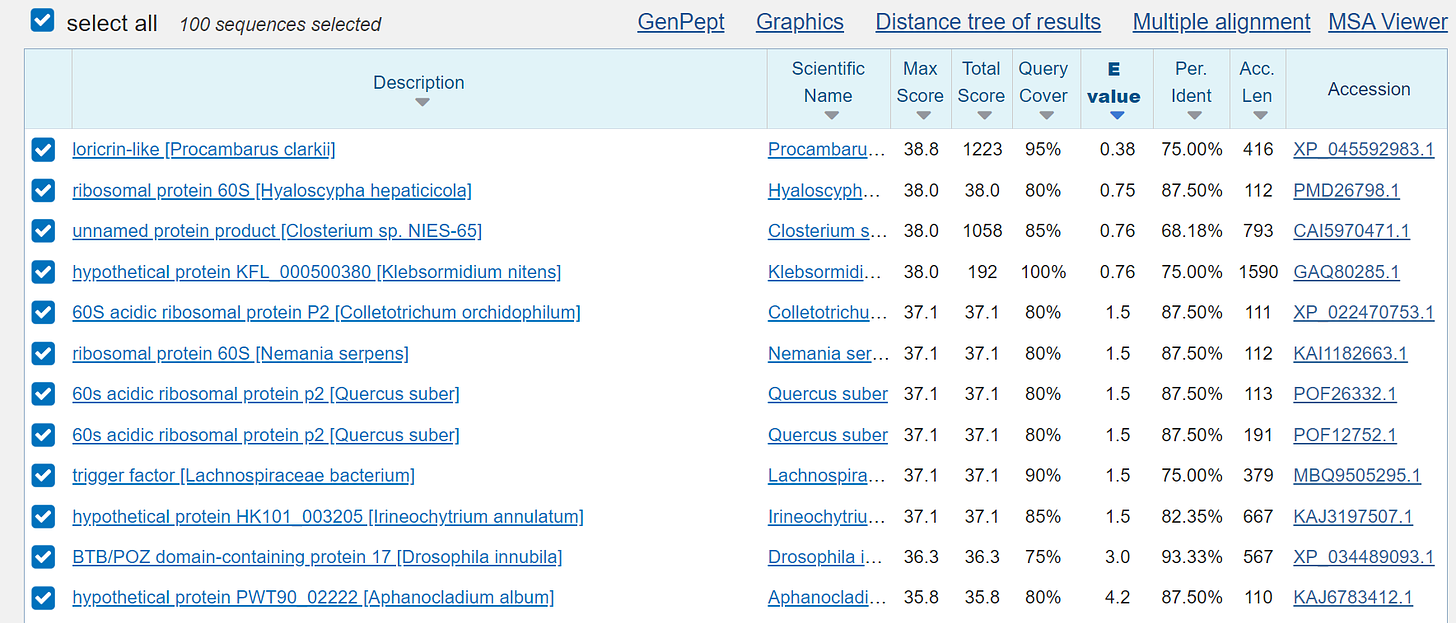
and the so-called "proteins", which of course are also only a fantasy:
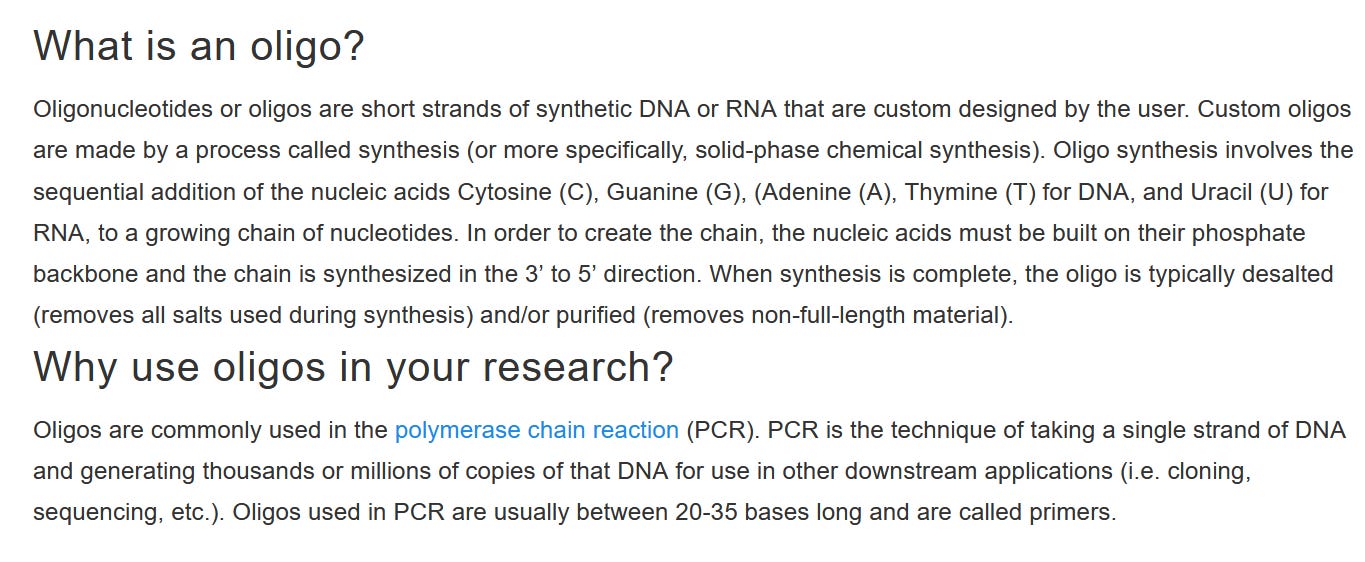
and so that you all know what oligonucleotides are - a synthetic, chemical preparation to lie to mankind and that for endless decades - a endless fraud!!!
https://www.thermofisher.com/at/en/home/brands/thermo-scientific/molecular-biology/molecular-biology-learning-center/molecular-biology-resource-library/spotlight-articles/using-oligos-in-research.html
None of this has anything to do with the reality of life of humans, animals, plants, etc.!!!
And it doesn't matter at all how many of these nuclotide sequences are strung together - no one can tell where they really came from!!!!
Read especially at !!Materials and Methods!!! - by these chemical additives the metabolism is switched off and everything is killed!!!
Materials and Methods
Chemicals
NPPB was obtained from Research Biochemicals, Inc. (Natick, MA). Other chemicals including tamoxifen, verapamil, DDFK, and fluorescein-conjugated wheat germ agglutinin (FITC-conjugated WGA, Triticum vulgaris) were obtained from Sigma Chemical Co. (St. Louis, MO). The antibody goat anti-multidrug resistance (mdr) protein (C129) was obtained from Research Diagnostics (Flanders, NJ).
RT-PCR Screening for P-Glycoprotein Isoforms
All animals were treated according to the ARVO Statement for the Use of Animals in Ophthalmic and Vision Research. Three- to 4-week-old Wistar rats were killed by CO2 asphyxiation and the eyes extracted. Whole lenses were extracted from the eyes in sterile dimethyl dicarbonate (DMDC)-treated phosphate-buffered saline (PBS: 2.7 mM KCl, 10 mM phosphate buffer, 137 mM NaCl [pH 7.4]). Lenses for RNA extraction were rolled on sterile filter paper to remove any adherent tissues, decapsulated to remove adherent epithelial cells, and immediately placed in a tissue storage reagent (RNAlater; Ambion, Austin, TX) before total RNA isolation. Total RNA was extracted with a kit (High Pure Tissue; Roche Molecular Biochemicals, Sydney, Australia) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. First strand synthesis and cDNA amplification were performed with an RT-PCR system (ThermoScript; Invitrogen, San Diego, CA). cDNA was synthesized from 1 μg total RNA with 5 mM oligo(dT)20 in 20-μL final reaction volumes. The RNA was denatured at 65°C for 5 minutes and cooled to 60°C before adding 10 μL of the following mix to give final concentrations of 1× cDNA synthesis buffer: 0.5 mM dithiothreitol (DTT), 1 mM dNTPs, and 40 U RNase inhibitor (RNaseOUT; Promega, Madison, WI). Reverse transcriptase (15 U; ThermoScript; Invitrogen) was added to the positive reaction mix. cDNA synthesis was performed at 60°C for 60 minutes. Up to 10% of the cDNA synthesis reaction was used for PCR amplification. Amplification was performed in 20- to 100-μL reactions, with final concentrations of 1× PCR buffer, 0.2 mM dNTPs, 0.05 U/μL Taq polymerase (Platinum Taq DNA Polymerase; Invitrogen), 1 to 5 mM MgCl2 and 0.2 to 1 μM sense and anti-sense primers from the P-glycoprotein primer sets listed in Table 1 . The DNA polymerase was activated by a 2-minute pre-PCR incubation at 94°C. Amplification was performed in 35 cycles of a three-step thermal cycling program (Omnigene; Hybaid, Ashford, UK): a 30-second period of denaturation at 94°C, 30 seconds’ annealing at 55°C, and extension at 72°C for 60 seconds. Amplified PCR products were analyzed by electrophoresis on 0.8% agarose gels, extracted from the gel using a kit (QIAquick; Qiagen, Valencia, CA) and subsequently sequenced by the dideoxy chain termination technique and a DNA sequencer (373A stretch DNA sequencer; Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA) on 5.25% polyacrylamide gels.
Northern Blot Analysis
Total RNA (5–10 μg) was loaded on 1% agarose denaturing gels (1% agarose (Ultrapure; Roche Molecular Biochemicals), 1× 3-(N-morpholino)propanesulfonic acid (MOPS), and 2.2 M formaldehyde. After electrophoresis at 5 V/cm for approximately 4 hours, total RNA was transferred onto a nylon membrane (Roche Molecular Biochemicals) overnight. The transferred denatured RNA was fixed onto the nylon membrane with a 3-minute exposure to UV light. The membrane was incubated in 6 mL of solution (DIG Easy Hyb; Roche Molecular Biochemicals) for 30 minutes before hybridization. Sequenced confirmed gene-specific DNA template (1 μg) was labeled with digoxigenin-11-dUTP in 20-μL reactions, using the DNA labeling kit (DIG; Roche Molecular Biochemicals). Double-stranded DIG labeled probes (10–20 ng/mL in DIG Easy HyB) were heat denatured at 99°C for 10 minutes, and hybridization was performed for approximately 3 to 4 hours at room temperature. The unbound probe was removed by washing the nylon membrane twice for 10 minutes (2× SSC and 0.1% SDS) with gentle agitation at room temperature. A further two washes (0.5× SSC and 0.1%SDS) were performed at the hybridization temperature for 10 minutes to remove nonspecific binding of the probe. The nylon membrane was washed in buffer A (100 mM maleic acid, 150 mM NaCl [pH 7.5]) at room temperature for 1 minute, and nonspecific antibody binding was blocked with a 30-minute incubation in blocking buffer (1% nonfat milk powder in buffer A). After labeling with the anti-DIG antibody diluted 1:20,000 (Roche Molecular Biochemicals), DNA-RNA hybrids were detected with chemiluminescence (CDP-star; Roche Molecular Biochemicals) exposed on autoradiographic film (Hyperfilm, ECL; Amersham, Little Chalfont, UK). Film was developed in an automatic processor (Curix 60, AGFA; Nunading, Victoria, Australia).
Detection of P-Glycoprotein by Western Blot Analysis and Immunocytochemistry
Crude membrane proteins were isolated from 10 adult rat lenses or from 1 adult rat brain. Tissue was homogenized in 10 mL of 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.4), 1 mM EDTA, 250 mM sucrose, 1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF), and 1 μg/mL leupeptin. The homogenate was centrifuged at 900g for 10 minutes at 4°C, and the resultant supernatant was centrifuged at 24,000 rpm (SW 40TI; Beckman Instruments, Fullerton, CA) for 75 minutes at 4°C. The pellet was solubilized by incubation for 1 hour in 500 μL buffer (100 mM Tris-HCl [pH 7.4], 1 mM EDTA, 0.5% TritonX-100, 0.5% sodium deoxycholate, and 1 mM PMSF). This homogenate was centrifuged at 14,000g for 10 minutes at 4°C, and the supernatant, containing the solubilized proteins, was collected in a separate tube. Proteins were separated on a 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel and transferred onto a nitrocellulose membrane by electrophoresis for 90 minutes at 170 mA. Transfer of proteins was confirmed by staining the nitrocellulose membrane for 4 minutes with Ponceau stain (1% Ponceau, 1% acetic acid in 100 mL filtered H2O (MilliQ; Millipore, Bedford, MA). Membranes were incubated overnight at room temperature in a blocking solution (1% BSA, 0.1% Tween20, 2 mM Tris-HCl, 140 mM NaCl [pH 7.6]) and subsequently incubated for 2 hours with goat anti-mdr protein antibody diluted 1:1000 (0.2 μg/mL in 1%BSA, Tris buffered saline [TBS]). Membranes were then exposed to biotinylated anti-goat IgG secondary antibody (Amersham) diluted 1:1000 for 1 hour, followed by streptavidin-horseradish peroxidase (HRP; Amersham) diluted 1:1000. After each incubation, the membranes were rinsed three times with water and washed three times for 15 minutes in TBS. The presence of P-glycoprotein was detected by enhanced chemiluminescence and exposed on autoradiographic film (Hyperfilm, ECL; Amersham).
For immunocytochemistry experiments, whole lenses were fixed for 16 hours in 2% paraformaldehyde in PBS. Wholemount capsules, with adherent epithelial cells, were fixed for 15 minutes. Lenses were briefly rinsed in PBS, incubated in 30% sucrose for 6 hours before incubating in optimal cutting temperature (OCT; Sakura Finetek, Tokyo, Japan) overnight. Whole lenses were mounted in OCT and frozen, and sections were cut at 16 μm. After three 5-minute washes in PBS, the lens sections or epithelial wholemounts were incubated in goat anti-mdr protein antibody diluted 1:50 (4 μg/mL in PBS) for 2 hours at room temperature. A control section, with goat anti-mdr protein antibody preincubated with peptide was also prepared. After three 5-minute washes in PBS, the sections were incubated with a secondary antibody, anti-goat IgG conjugated to red dye (Rhodamine Red; Molecular Probes, Eugene, OR) diluted 1:100. Lens sections were washed with three 15-minute washes in 1× PBS before the sections were mounted onto slides with antifading reagent (FluoroGuard; Bio-Rad, Richmond, CA). Sections were viewed with a confocal laser scanning microscope (TCS 4D, Leica Lasertechnik, Heidelberg, Germany) fitted with an argon-krypton mixed gas laser. The software accompanying the microscope was used to record confocal microscopy images (SCAware; Leica).



Thank you, Mary-Ann! Lots of details here that are not exactly public knowledge...